Indo-European Languages Origin: Tracing Linguistic Roots
The origin of Indo-European languages has captivated linguists and historians for centuries, revealing a rich tapestry of cultural evolution and migration. Recent studies suggest that the ancestry of these languages traces back to the Caucasus Lower Volga people, located in present-day Russia about 6,500 years ago. These early speakers, associated with the influential Yamnaya culture, are believed to have contributed significantly to the spread of this vast family of languages, which includes over 400 distinct tongues spoken by 40% of the global population today. Genetic evidence supports their emergent role in language dynamics, shedding light on the intricate pathways of language evolution. Through archaeological findings and language evolution studies, a clearer picture emerges of how these ancient peoples shaped the linguistic landscape we know today.
The roots of the Indo-European language family stretch back thousands of years, intertwining with the ancient civilizations of the Eurasian steppe. Scholars have long explored the ancestral connections among various languages, often referencing the Caucasus Lower Volga inhabitants as foundational to this linguistic lineage. Their legacy is not merely confined to words; it encapsulates a broader cultural narrative, enriched by the Yamnaya culture’s innovations in mobility and pastoralism. Recent genetic research has provided vital insights into the demographic shifts that facilitated the dispersal of these languages across continents. By examining the interplay of language, genetics, and archaeology, we enhance our understanding of language origins and their subsequent evolution throughout history.
The Role of the Caucasus Lower Volga People in Indo-European Language Development
The Caucasus Lower Volga people have been identified as pivotal in the development of the Indo-European language family, which encompasses languages spoken by over 3 billion individuals today. These ancient groups, dated back to approximately 6,500 years ago, inhabited regions around the lower Volga River, where they came into contact with various neighboring cultures. This mingling significantly influenced the evolution of their language and culture, serving as a foundational lineage to subsequent Indo-European speakers, including the well-known Yamnaya culture. Genetic studies indicate that these early speakers not only had their unique linguistic traits but also assimilated influences from surrounding populations, marking a dynamic process of language evolution in the prehistoric period.
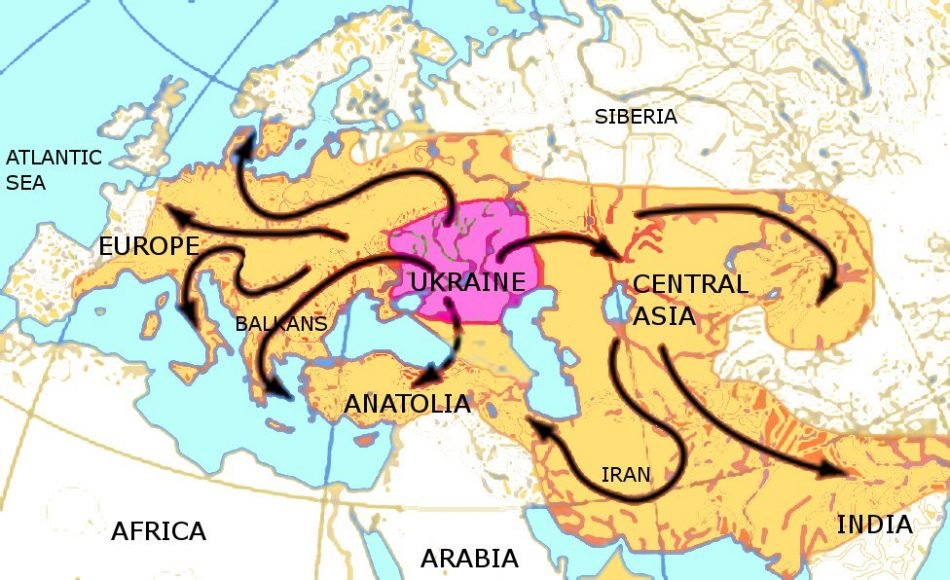
Understanding the contributions of the Caucasus Lower Volga people sheds light on the broader linguistic landscape of Indo-European languages. Archaeological findings suggest that their societal structures and burial practices, such as kurgan constructions, helped solidify their identity. Over time, their innovations and interactions prompted the migration of language and culture across vast distances—from the steppes of Eurasia to regions as far as Ireland and India. This remarkable dispersal of languages can directly be traced to the foundational role played by these ancient groups, reinforcing the idea that language is intimately tied to human migration and cultural exchange.
Genetic Evidence Supporting Indo-European Language Theories
Recent genetic evidence has provided critical insights into the origins of Indo-European languages, aligning with historical linguistic theories. The pivotal studies reported in *Nature* revealed that the DNA of the Caucasus Lower Volga people matched expectations of the Yamnaya’s genetic profile, clarifying their status as early speakers of the proto-Indo-European language. The combination of genetic analysis and archaeological findings has enabled researchers to construct a clearer picture of how language and genetics intertwine. Such breakthroughs indicate that linguistic similarities across Indo-European languages may stem from shared ancestry and migration patterns defined by these early peoples.
The implications of this genetic evidence extend beyond academic linguistics; they serve as a fascinating reflection of human history and societal evolution. Over the past few decades, researchers have made substantial advances in understanding how migrations, such as those undertaken by the Yamnaya culture, corresponded with vast linguistic shifts. For instance, the significant population replacement documented in regions like Germany and Britain provides a compelling narrative about how the Indo-European languages spread and transformed. This synthesis of genetic data with linguistic research underscores the profound influences that ancient migrations have had on modern languages.
The Yamnaya Culture: Pioneers of Language and Mobility
The Yamnaya culture has often been heralded as a cornerstone in the narrative of Indo-European language dispersal. Situated on the Eurasian steppes, these pastoralists were not merely herders; they were innovators who changed the trajectory of human mobility and cultural exchange. Utilizing oxen-towed wagons for transportation, the Yamnaya expanded their reach across continents, engaging in trade, warfare, and cultural intermingling—activities that played a definitive role in the spread of the proto-Indo-European language. Their ability to navigate varied terrains and climates facilitated diverse interactions, creating a fertile ground for linguistic evolution.
Moreover, the Yamnaya’s practices, such as their burial customs and social structures, contributed to the establishment of a coherent cultural identity, which resonated through their language. They were integral to a transformative period marked by mobility and exchange, and their genetic legacy persists in modern European populations. By examining the Yamnaya culture’s profound impact, scholars can better understand not only the development of Indo-European languages but also the profound effects of ancient migrations on contemporary societies.
Archaeological Findings and Language Dynamics
Archaeological findings have played a crucial role in understanding the dynamics of ancient languages. Excavations in areas inhabited by the Caucasus Lower Volga people and the Yamnaya culture have yielded artifacts and burial sites that reveal the complex interplay between culture and communication. For instance, the discovery of kurgans provides insight into funeral practices and social hierarchies, which in turn afford clues about the sociolinguistic environment of these early communities. The materials unearthed allow researchers to draw connections between linguistic developments and the cultural practices that accompanied them.
Furthermore, such archaeological evidence enhances our understanding of language evolution amid shifting demographics. As populations migrated and intermixed, linguistic features evolved, leading to the diverse forms we recognize in the Indo-European family today. The study of these archaeological sites reveals not only the rituals and daily lives of ancient peoples but also the nuanced fabric of language as it adapted to encompass new influences and incorporate elements from different dialects and cultures.
The Historic Intersection of Genetics and Language Studies
The intersection of genetics and language studies marks a groundbreaking era in understanding the origins of modern languages. By utilizing ancient DNA sequencing techniques, researchers can map the genetic lineage of populations such as the Yamnaya and the Caucasus Lower Volga people, correlating these findings to linguistic developments. This innovative approach provides unprecedented clarity in understanding the relationships between ancient languages and their speakers, revolutionizing conventional theories about language origins.
Additionally, this multidisciplinary study emphasizes the interconnectedness of human history, wherein genetics informs linguistic evolution and vice versa. As geneticists collaborate with linguists and archaeologists, a more comprehensive picture of language dynamics emerges. The shared findings contribute to a cohesive narrative that portrays language as a living entity, shaped by genetic history and cultural exchanges across millennia—a testament to the complex tapestry of human civilization.
Cultural Traditions and Linguistic Evolution
Cultural traditions are pivotal in shaping language, influencing how communities express themselves and interact with one another. The ancient practices of the Caucasus Lower Volga people and the Yamnaya represent vital examples of how cultural heritage can inform the linguistic characteristics of a society. For example, their burial customs—such as kurgans—reflect a rich cultural identity that has endured through generations, potentially influencing the language used around rituals and community gatherings.
Moreover, the dynamics of these traditions facilitate language evolution as they encounter new cultures and languages. As groups intermingle—through trade, migration, or conflict—language patterns adapt, expanding vernaculars and introducing new vocabulary, which can be traced within the Indo-European language family. This intertwining of culture and language is a significant area of study, highlighting how preserving cultural identity can intrinsically alter the linguistic landscape of a population.
Challenges in Studying Indo-European Language Origins
Despite the advances made in tracing the origins of Indo-European languages, researchers face substantial challenges stemming from historical and geopolitical factors. The interplay of politics, particularly illustrated by the Russia-Ukraine conflict, has made it increasingly difficult for scholars to collaborate across borders. Access to archaeological sites and historical data may become restricted, complicating efforts to confirm findings or conduct further research. This division poses a significant barrier to understanding the complete picture of linguistic and genetic interactions that shaped these ancient languages.
In addition, the complexities inherent in ancient DNA analysis can present obstacles to deriving accurate conclusions. As genetic data is scrutinized and interpreted, researchers must consider how environmental factors, varying populations, and historical migrations influence genetic signatures. Navigating these challenges requires innovative methodologies and a commitment to interdisciplinary collaboration, ensuring that the comprehensive study of Indo-European languages continues to advance despite other limitations.
Future Directions in Indo-European Language Studies
Looking forward, the studies of Indo-European languages are poised to evolve through emerging technologies and methodologies. The integration of advanced genetic sequencing techniques coupled with computational linguistics opens up exciting possibilities for deeper insights into the evolution of these diverse language systems. Researchers aim to refine the understanding of how languages spread and transformed, focusing on the nuances of dialectal variations and lexical changes over time, which are essential for a thorough grasp of language dynamics.
Moreover, interdisciplinary collaborations will likely play a critical role in future research endeavors. As linguists partner with geneticists, archaeologists, and anthropologists, a holistic approach can be established, drawing connections between genetics, culture, and language. This comprehensive toolkit will not only enhance our understanding of Indo-European languages but also enrich our comprehension of human history as a whole, uncovering the intricate links among ancestry, culture, and linguistic evolution.
The Importance of Collaborative Research in Uncovering Linguistic History
Collaborative research is essential for unveiling the complex tapestry of linguistic history, particularly in projects tracing the origins of Indo-European languages. As evidence from various scientific disciplines converges—be it genetic, archaeological, or linguistic—scholars can create a multi-faceted understanding of how languages and cultures evolved. The work conducted by teams like those at Harvard illustrates the power of interdisciplinary studies, as diverse expertise brings new perspectives on familiar problems.
Furthermore, collaborative initiatives can bridge gaps between regions and scholarly communities impacted by geopolitical tensions. By sharing data and findings on platforms that promote inclusivity and transparency, researchers contribute to a broader dialogue about the historical movements of people and languages. This collective effort ensures that new discoveries yield valuable insights into human history, enhancing the understanding of how language is a powerful vehicle for both cultural identity and shared heritage.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the significance of the Caucasus Lower Volga people in the origin of Indo-European languages?
The Caucasus Lower Volga people are significant as they are identified as the original speakers of the proto-Indo-European language, dating back approximately 6,500 years. Their genetic evidence and archaeological findings indicate they lived in present-day Russia and played a critical role in the early linguistic evolution that led to the diverse Indo-European languages spoken by over 40% of the global population today.
How does genetic evidence support the Yamnaya culture as a key contributor to Indo-European languages?
Genetic evidence suggests that the Yamnaya culture, which emerged from the Caucasus Lower Volga region, was instrumental in dispersing Indo-European languages across Europe and Asia. These nomadic pastoralists were linked genetically to modern European populations, demonstrating how they shared their language and culture during migrations from the steppe into various territories.
What role did archaeological findings play in studying the language dynamics of Indo-European origins?
Archaeological findings, such as burial mounds and settlement patterns, have been essential in understanding the cultural practices of the Caucasus Lower Volga people and the Yamnaya culture. These findings provide a physical context for language evolution studies, revealing how these early communities may have spread their languages alongside their genetic and cultural practices.
What recent advancements have been made in language evolution study concerning Indo-European origins?
Recent advancements in language evolution study, particularly the groundbreaking research published in the journal *Nature*, have utilized ancient DNA analysis to trace the origins of Indo-European languages back to the Caucasus Lower Volga people and their interaction with the Yamnaya culture. This research provides a clearer genetic framework that aligns with historical linguistic theories.
How did the interaction of the Caucasus Lower Volga people with other groups influence Indo-European language development?
The interaction of the Caucasus Lower Volga people with neighboring groups, as revealed by genetic studies, likely facilitated the development and diversification of Indo-European languages. This mixing of cultures and languages over time contributed to the complex family of languages that emerged from the proto-Indo-European roots across Europe and Asia.
What can be inferred about the social structure of Indo-European speakers based on archaeological evidence?
Archaeological evidence, such as the discovery of kurgans (burial mounds), suggests that Indo-European speakers, particularly the Yamnaya culture, had a structured society with specific burial rituals and social hierarchies. These findings provide insights into their cultural and social organization, which likely influenced the spread and adaptation of their languages.
Why is the study of genetic footprints critical in understanding the spread of Indo-European languages?
Studying genetic footprints is critical as it allows researchers to trace the migrations and interactions of early Indo-European speakers, including the Caucasus Lower Volga people and the Yamnaya. By mapping these genetic connections, researchers can illustrate how languages spread alongside these populations, enriching our understanding of historical linguistics and migration patterns.
What impact did the migration of Indo-European language speakers have on Europe’s demographic landscape?
The migration of Indo-European language speakers, particularly those from the Yamnaya culture, had a profound impact on Europe’s demographic landscape, contributing to significant population replacements and cultural shifts. Genetic studies have shown that this group brought new languages and practices, which reshaped the identities of many modern European populations.
| Key Findings | Details |
|---|---|
| Origin of Indo-European languages | Identified as originating from the Caucasus Lower Volga people in Russia around 6,500 years ago. |
| Key Researchers | Nick Patterson, Iosif Lazaridis, David Reich, among others. |
| Significance of Findings | This research solves a long-standing puzzle in the linguistic history of Indo-European languages and establishes genetic links to the languages spoken today. |
| Cultural Practices | The Yamnaya were known for pioneering horseback herding and using oxen-towed wagons. |
| Genetic Evidence | DNA analysis links modern Europeans to ancient populations, revealing significant migrations and genetic mixing influencing current populations. |
| Contemporary Issues | The ongoing Russia-Ukraine war complicates collaborative research, with findings split between two major papers involving researchers from both countries. |
Summary
The origin of Indo-European languages reveals a fascinating narrative entwined in history, linguistics, and genetics. Identified as coming from the Caucasus Lower Volga region approximately 6,500 years ago, these languages initially spoken by a small population have significantly influenced global linguistic patterns. The groundbreaking studies emphasize the importance of genetic evidence in tracing the origins of over 400 languages spoken by a vast portion of the world today, showcasing the intricate migration and mixing of ancient peoples that shaped modern European and Asian demographics.